In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital finance, decentralized payment networks have emerged as a revolutionary concept that promises to reshape how we conduct transactions. By removing intermediaries and leveraging blockchain technology, these networks enable seamless peer-to-peer transfers of value.
In this blog post, we will explore what decentralized payment networks are, how they function, and their potential impact on the future of finance. Uncover insights with KwickBit!
What Is a Decentralized Payment Network?
A decentralized payment network is a system that facilitates transactions directly between users without relying on a central authority, such as banks or financial institutions. Unlike traditional payment systems, which typically require intermediaries to process and verify transactions, decentralized payment networks operate on a distributed ledger technology (DLT), allowing participants to transact directly with one another.
This innovative approach not only enhances transaction speed but also reduces costs associated with traditional payment methods. By leveraging a network of nodes to verify transactions, these systems ensure security and transparency while minimizing the risk of fraud.
How Decentralized Payment Networks Work?
Decentralized payment networks leverage various technologies and protocols to facilitate transactions, and their operation can be summarized through several key components and processes:
At the heart of these networks is blockchain technology, a distributed ledger that securely and transparently records all transactions. Transactions are grouped into blocks, which are then linked to form a chain. This structure ensures that once a transaction is recorded, it becomes immutable, providing a high level of security and trust.
Transactions within a decentralized payment network occur peer-to-peer, meaning they take place directly between users without the need for intermediaries. When a user initiates a payment, it is broadcast to the network, where nodes work to validate and confirm the transaction. This peer-to-peer model not only accelerates the transaction process but also reduces fees, making it an attractive option for users.
To maintain the integrity of the network, decentralized payment systems employ consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). These mechanisms require participants (nodes) to reach an agreement on the validity of transactions before they are added to the blockchain. This collective verification process enhances security and helps prevent fraudulent activities.
Furthermore, many decentralized payment networks are designed with interoperability in mind, allowing users to move assets seamlessly across different blockchains. This capability eliminates the need for third-party exchanges, simplifying the management of digital assets for users.
How Is a Decentralized Payment Network Different From a Centralized Payment Network?
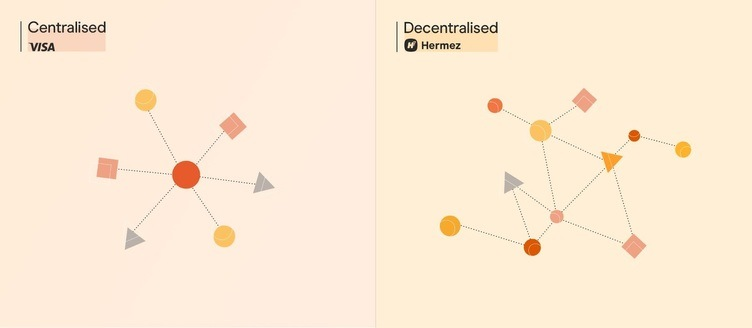
Centralized payment networks encompass various entities, including banks and remittance companies. In these systems, each bank maintains a private ledger that records all transactions made by its customers. Additionally, banks have accounts with other banks and central banks, allowing for cross-bank transfers. For example, when someone initiates an international bank transfer, the involved banks will debit and credit their respective accounts to complete the transaction.
Historically, banks have provided a high level of security compared to alternative options, such as keeping cash at home. However, the rise of the internet has also led to increased incidents of hacking and data breaches. If a malicious actor gains access to a bank’s central ledger, they could potentially alter the balances of all customers and even manipulate the records of other banks.
In contrast, decentralized payment networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum utilize a fundamentally different approach. They operate on a public ledger that is continuously recorded and verified by numerous nodes within the network. The immutability of transaction records in these blockchains significantly reduces the risk of fraud, making them a more secure option for transferring value in the digital age compared to traditional banking systems.
What Are the Benefits of Decentralized Payments?
Decentralized payment networks offer several significant advantages over their centralized counterparts:
Cost-Effective and Transparent Transactions: Decentralized payment networks are generally cheaper, more transparent, and more reliable than traditional banking systems. While blockchains like Ethereum may face criticism for high fees during congestion, international bank transfers often incur substantial costs. For example, sending money from Germany to Brazil involves not only transfer fees—typically a percentage of the total amount—but also potential currency exchange rates from euros to reais. In contrast, using Bitcoin or Ethereum eliminates intermediaries, making these cryptocurrencies a more user-friendly option. Additionally, traditional international transfers can take days to settle, as funds pass through multiple institutions, often taking three to four business days to complete. Decentralized networks, however, offer quicker transaction times and are less prone to hacks compared to centralized databases.
Increased Financial Inclusion: Decentralized payment networks have the potential to bring financial services to millions of people in developing nations. Billions remain unbanked, lacking access to the global financial system due to factors like inadequate identification, geographical barriers, or official documentation. However, the widespread availability of internet access through mobile devices allows anyone with a phone to open a Bitcoin or Ethereum wallet, gaining instant access to money transfers and decentralized finance services.
Empowerment and Control Over Finances: Decentralized payment networks empower individuals to take control of their money. In many developing countries, high levels of corruption and weak institutions make it challenging for citizens to manage their finances. Mismanagement by corrupt elites can lead to currency collapse, further disenfranchising the population. Decentralized payment networks enable users to choose which currencies to operate in and provide censorship resistance, ensuring that no one can prevent someone from opening a wallet and participating in the network.
Decentralized Payment Protocols in the Internet of Value

Decentralized payment protocols represent a significant shift in the way we conduct digital transactions. Moving away from centralized systems and the isolation of traditional blockchains, these protocols streamline processes by eliminating intermediaries and allowing direct transactions between peers.
At the core of decentralized payment protocols is a network of nodes that verify and validate transactions, rather than relying on a single authority. This contrasts sharply with traditional payment systems, where banks and central entities typically oversee transaction processing, often resulting in delays and additional costs.
One of the most intriguing aspects of these protocols is their design for interoperability across various blockchains. This flexibility enables users to move their assets seamlessly between different networks without depending on third-party exchanges or complex conversion processes.
Security is another critical consideration in the development of decentralized payment protocols. While some systems lean heavily on smart contracts to enforce transaction terms, decentralized payment protocols prioritize simplicity and robustness. They employ advanced cryptographic techniques and consensus algorithms to ensure secure and reliable transactions.
How Decentralized Payment Protocols Work Within the Internet of Value
Decentralized payment systems leverage blockchain technology to enable fast and easy transfers of money across the internet. They are adaptable and cater to a variety of needs, including the integration of cryptocurrency payments for businesses.
Conclusion
So now you’ve learned about What Is a Decentralized Payment Network? KwickBit hopes this article will provide you with more useful information.
Decentralized payment networks represent a significant leap forward in the way we handle transactions. By leveraging blockchain technology and peer-to-peer models, these networks offer numerous benefits, including lower costs, enhanced security, and faster transaction speeds.
As we move towards a more interconnected and digital financial landscape, understanding decentralized payment networks will be crucial for both consumers and businesses alike. Embracing these innovations can lead to a more efficient and equitable financial system for all.
KwickBit – Non-custodial Payment Gateway
Read more:
- What Are Cryptocurrencies? What You Need to Know
- What Is Crypto In Business? Why More Businesses Should Consider Using Cryptocurrency
- What is Payment in E-Commerce? Demystifying E-Commerce Payments
